what are the 3 components of high quality cpr ,while performing high quality cpr on an adult,what are the 3 components of high quality cpr, Effective chest compressions are the most important component of Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR). High quality CPR involves rescuers being aware of how to deliver effective chest compressions to a victim in order .
Best Designer Replica sites. For replica bags, replica sneakers and jerseys, Dhgate is the number #1 replica online wholesaler. Dhgate sellers sell in bulk as well. Alibaba .
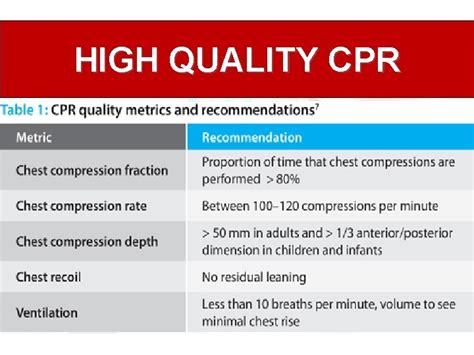
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a life-saving skill that everyone should be familiar with, whether they’re a healthcare professional or an ordinary bystander. Effective CPR can significantly improve the chances of survival for a person who has experienced cardiac arrest, making it an essential tool in emergency situations. To perform high-quality CPR, however, it is necessary to understand its core components.
In this article, we will explore the three fundamental components of high-quality CPR, discuss the necessary techniques for adult patients, the importance of timing, and the correct criteria for when and how to switch responders during the procedure. Furthermore, we will break down the characteristics of high-quality CPR and emphasize its role in increasing the likelihood of survival in cases of sudden cardiac arrest.
1. Chest Compressions
The first and perhaps most critical component of high-quality CPR is chest compressions. Chest compressions serve to artificially circulate blood throughout the body, particularly to vital organs such as the brain and heart, when the heart is no longer pumping blood effectively. Inadequate chest compressions can lead to poor blood flow, which ultimately decreases the chances of survival.
# Guidelines for Effective Chest Compressions:
- Rate: CPR compressions should be delivered at a rate of 100-120 compressions per minute. This rate is optimal for ensuring that blood circulation is restored without tiring the rescuer. This range is consistent with guidelines provided by organizations like the American Heart Association (AHA) and the American Red Cross.
- Depth: Compressions should be deep enough to allow for a proper volume of blood to be pumped through the circulatory system. For an adult, the recommended compression depth is at least 2 inches (5 cm), but no deeper than 2.4 inches (6 cm).
- Full Recoil: One of the key elements of chest compressions is allowing the chest to fully recoil after each compression. Full recoil means that the chest returns to its normal position before the next compression. Incomplete recoil reduces the effectiveness of CPR by limiting blood return to the heart and decreases overall perfusion.
- Body Position: For adult victims, the rescuer should kneel beside the person, positioning their hands on the lower half of the breastbone (sternum). It is essential to use proper body mechanics to avoid injury and ensure sufficient force.
# Why Are Chest Compressions So Important?
The chest compression technique in CPR is a vital factor because it helps maintain the flow of oxygenated blood to the brain and heart. In cases of sudden cardiac arrest, the heart stops beating, and without proper circulation, the brain can suffer irreversible damage within minutes. Chest compressions offer a temporary solution until professional medical responders can take over or until an automatic external defibrillator (AED) is available to administer a shock.
2. Airway Management
The second component of high-quality CPR involves ensuring that the patient's airway is open so that air can be properly delivered to the lungs. While chest compressions are essential for circulating blood, effective airway management is equally critical in ensuring that oxygen reaches the body’s organs.
# Steps for Opening the Airway:
- Head-Tilt, Chin-Lift Maneuver: This technique should be used to open the airway. Place one hand on the victim's forehead and gently tilt the head back, while using the other hand to lift the chin upwards. This maneuver helps to clear any obstruction in the airway (such as the tongue) and facilitates unobstructed breathing.
- Jaw Thrust Maneuver (for trauma victims): In cases of suspected spinal injuries or trauma, the jaw thrust maneuver is recommended. This maneuver is less likely to aggravate any potential neck injuries. To perform the jaw thrust, the rescuer should position their hands on both sides of the patient’s head and push the jaw forward.
# Airway Considerations:
- Obstructions: If the patient has any visible obstruction (such as vomit, blood, or foreign objects) blocking their airway, the rescuer should try to clear it immediately.
- Breathing: After ensuring the airway is open, the next step is to check for breathing. If the victim is not breathing or is only gasping, it is critical to begin rescue breathing (if trained to do so) or continue with chest compressions.
- Rescue Breathing (optional but recommended): If you are trained in rescue breathing, it’s important to provide breaths in conjunction with compressions. For adults, give 2 rescue breaths for every 30 chest compressions. Ensure that each breath lasts about 1 second and makes the chest rise visibly.

what are the 3 components of high quality cpr Discover Hong Kong's top fake markets, where you can find designer-inspired deals without the designer price tags. Read more information here.
what are the 3 components of high quality cpr - while performing high quality cpr on an adult